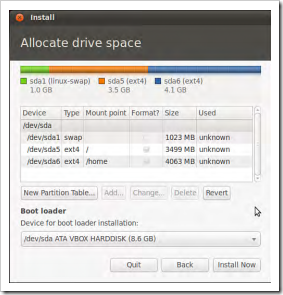
We recommend 3 simple partitions to setup when installing Ubuntu for the first time
- Swap Partition
- Root Partition
- Home Partition
home partition where data for each user on the system will be stored.
The Swap Partition
The swap partition is used for times when there is not enough memory for running processes, so stored information from RAM is send to the hard drive and use that swap space as extra RAM. This was very useful in old machines that used little memory. But we will use it mainly for storing information during suspend and hibernate mode, which can be used instead of turning off your computer.
Suspend saves your current system state to RAM and then turns off the power to most of the system, but maintains just enough power use to keep that state saved in RAM.
When you restart your system, it comes back quickly and to the same state it was in.
Hibernate saves your current system state to the hard disk. These days, it is just as fast to boot from scratch as it is to hibernate and restore, so there isn’t much point in using it.
We recommend a swap partition to be about 1.5 to 2 times the size of your current Ram Memory, i.e.: If you have 4GB of Ram, your Swap must be from 6GB to 8GB
The Root Partition
This is where all your operating system files will live.You will see it as a / and we recommend making a partition of at least 5GB
The Home Partition
We recommend having it on a separate partition because it enables you to install a different Linux
distribution or a different release of Ubuntu on your / partition while retaining your user data. It is also handy when you want to backup your files or when you install Ubuntu on another computer and you want all your data to go along in the new computer.
We recommend using the rest of your Hard Disk Drive for the home partition.